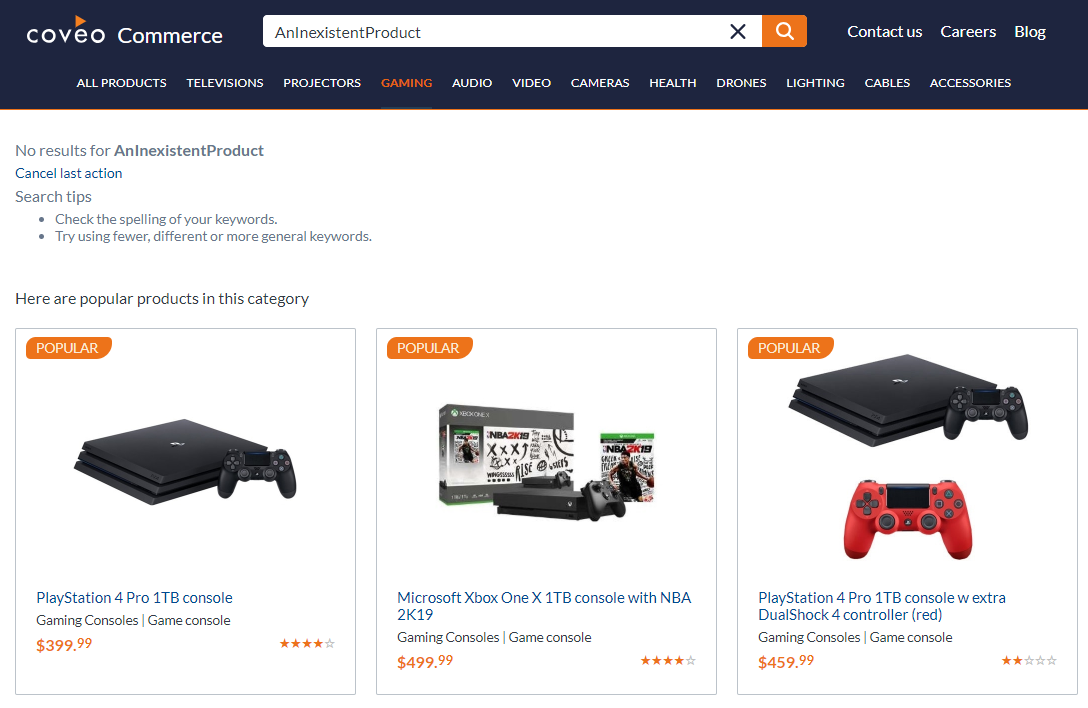
There are only a few things more frustrating than getting a simple no results message when you are searching something. Luckily, with the Coveo JavaScript Search Framework (JS UI), it is very easy to propose popular search results to the visitor when that happens by adding a few components, lines of JavaScript, and CSS statements. It is especially important on a commerce website where all opportunities to display products may result in increased sales.
Starting Point
For this example, let’s start with a simple search interface.
<div id="search"
class="CoveoSearchInterface"
data-enable-history="true"
data-pipeline="CommerceML">
...
<div class="coveo-tab-section">
<div class="CoveoTab"
data-id="default"
data-caption="All Products"></div>
<div class="CoveoTab"
data-id="Televisions"
data-caption="Televisions"
data-constant="true"
data-expression="@cccategory=Televisions"></div>
<div class="CoveoTab"
data-id="Projectors"
data-caption="Projectors"
data-constant="true"
data-expression="@cccategory=Projectors"></div>
...
</div>
...
<div class="coveo-results-column">
<div class="coveo-results-header">
<div class="coveo-summary-section">
<span class="CoveoQuerySummary"></span>
<span class="CoveoQueryDuration"></span>
</div>
<div class="CoveoResultLayout"></div>
...
</div>
<div class="CoveoResultList" data-layout="card">
<script class="result-template" type="text/underscore">
<div class="coveo-result-frame">
...
</div>
</script>
</div>
<div class="CoveoResultList" data-layout="list">
<script class="result-template" type="text/underscore">
<div class="coveo-result-frame">
...
</div>
</script>
</div>
...
</div>
<div class="CoveoAnalytics"></div>
</div>
<script>
var mainSearchInterfaceElement = document.querySelector('#search');
Coveo.SearchEndpoint.configureCloudV2Endpoint('default', 'YOUR_API_KEY');
Coveo.init(mainSearchInterfaceElement);
</script>
This main search interface has:
data-enable-history="true"to enable state management- Many
CoveoTabcomponents with constant expressions, except the first one for all products (default) - A
CoveoQuerySummarycomponent that displays the standard no results message - A
CoveoResultLayoutcomponent to switch between card and list results layout - Two
CoveoResultListcomponent for the card and list layouts - Inline result templates inside the result lists
- A
CoveoAnalyticscomponent to ensure searches and clicks are tracked in Coveo Cloud - A simple initialization script
Goal
When the visitor query returns no results:
- Display the 3 most popular products of the currently selected category (tab)
- Do not display popular products if the “All Products” category (first tab) is selected
Extract the Result Templates
The popular products must share the same result template than the regular products. So, the first step is to extract the main search interface result templates for reusability. Result templates can be defined anywhere in the DOM and referenced by their id. Referencing a result template is done with the loadTemplate(templateId: string, condition?: boolean, contextObject?: any) template helper function in UnderscoreJS code. The condition and contextObject parameters are optional.
<script id="DefaultCardTemplate" class="result-template" type="text/underscore">
<div class="coveo-result-frame">
...
</div>
</script>
<script id="DefaultListTemplate" class="result-template" type="text/underscore">
<div class="coveo-result-frame">
...
</div>
</script>
<div id="search"
class="CoveoSearchInterface"
data-enable-history="true"
data-pipeline="CommerceML">
...
<div class="coveo-results-column">
...
<div class="CoveoResultList" data-layout="card">
<script class="result-template" type="text/underscore">
<%= loadTemplate('DefaultCardTemplate') %>
</script>
</div>
<div class="CoveoResultList" data-layout="list">
<script class="result-template" type="text/underscore">
<%= loadTemplate('DefaultListTemplate') %>
</script>
</div>
...
</div>
<div class="CoveoAnalytics"></div>
</div>
In the example above, the extracted card result template have an id attribute value of DefaultCardTemplate and is referenced by calling <%= loadTemplate('DefaultCardTemplate') %>.
Popular Results
Popular results might mean different things to different people. For Coveo, it is results that were clicked the most for a given query. This is tracked by Coveo Usage Analytics on the main search interface. Popular results can be surfaced (boosted) by an Automatic Relevance Tuning (ART) machine learning model in the Coveo query pipeline used by a search interface. In this example, the main search interface is using the CommerceML query pipeline. All queries using this pipeline will have boosted popular results.
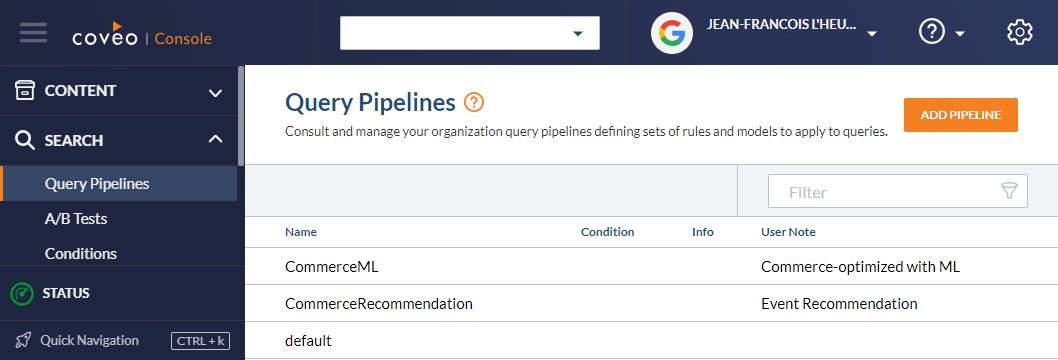
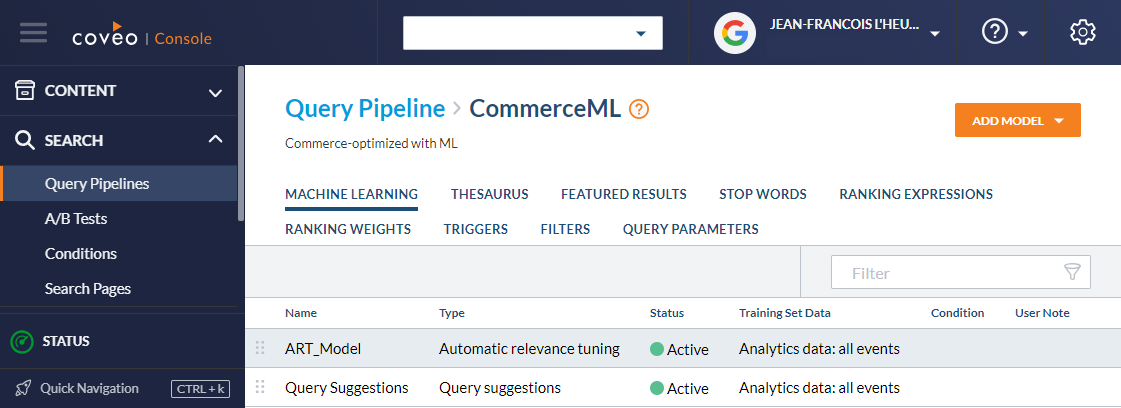
The popular products feature can be implemented by adding a second search interface that uses the same query pipeline.
<div id="search"
class="CoveoSearchInterface"
data-enable-history="true"
data-pipeline="CommerceML">
...
</div>
<div id="NoResultsPopularSection" class="no-results-popular-section hidden">
<div id="NoResultsPopularSearch"
class="CoveoSearchInterface"
data-results-per-page="3"
data-auto-trigger-query="false"
data-pipeline="CommerceML">
<div class="coveo-results-column">
<div class="coveo-results-header">
<div class="coveo-query-summary-no-results-string">
Here are popular products in this category
</div>
<div class="CoveoResultLayout"></div>
</div>
<div class="CoveoResultList" data-layout="card">
<script class="result-template" type="text/underscore">
<%= loadTemplate('DefaultCardTemplate') %>
</script>
</div>
<div class="CoveoResultList" data-layout="list">
<script class="result-template" type="text/underscore">
<%= loadTemplate('DefaultListTemplate') %>
</script>
</div>
</div>
<div class="CoveoAnalytics"></div>
</div>
</div>
It does not have a search box and does not automatically trigger a query when initialized thanks to the data-auto-trigger-query="false" option. It has 2 result lists and support for Coveo usage analytics.
The layout is very simple with a results column, a results header, and header message. All those containers are defined only for their associated CSS styles.
The CoveoResultLayout component that allows to switch between card and list layout is included just to allow the two layouts. It will later be hidden with CSS.
Styling
Main Search Interface CSS
Some CSS rules were needed to offer a unified experience across devices and reduce the whitespace between the standard no results message and the recommended results.
/* By default, the no results message is displayed on the right of the facets section. Ensure the no results message has no margin-left */
.CoveoSearchInterface .coveo-results-column.coveo-no-results {
max-width: none;
clear: both;
}
/* Remove margins on empty result lists */
.coveo-no-results .CoveoResultList {
margin-top: 0;
margin-bottom: 0;
}
/* Ensure empty pagers are not taking any vertical space */
.coveo-no-results .CoveoPager {
display: none;
}
Popular Results CSS
Some CSS rules were also needed for the new search interface.
/* Ensure the initialization placeholder animation is hidden */
.no-results-popular-section.hidden {
display: none;
}
/* Hide the popular search interface layout switcher */
.no-results-popular-section .CoveoResultLayout {
display: none;
}
/* Remove line under the section title */
.no-results-popular-section .coveo-results-header {
box-shadow: none;
}
Business Logic
Helpers
To help with code readability, helpers were created around the Coveo APIs.
function getSearchInterfaceLayout(searchInterfaceElement) {
return Coveo.state(searchInterfaceElement).get('layout');
}
function setSearchInterfaceLayout(searchInterfaceElement, layout) {
Coveo.state(searchInterfaceElement).set('layout', layout);
}
function hideElement(element) {
element.classList.add('hidden');
}
function showElement(element) {
element.classList.remove('hidden');
}
function getCurrentTab(searchInterfaceElement) {
var currentTabId = Coveo.state(searchInterfaceElement, 't');
var currentTabElement = document.querySelector('.CoveoTab[data-id="'+ currentTabId + '"]');
return Coveo.get(currentTabElement, 'Tab');
}
Main Search Interface Code
To know when the main search interface has no results, a querySuccess event handler is required. When that happens, and a category tab is selected:
- The result layout of the main search interface is copied to the popular results search interface
- The query is executed for the popular results search interface
- The popular results search interface is displayed
var mainSearchInterfaceElement = document.querySelector('#search');
var noResultsPopularSection = document.querySelector('#NoResultsPopularSection');
var noResultsPopularSearchElement = document.querySelector('#NoResultsPopularSearch');
Coveo.$$(mainSearchInterfaceElement).on(Coveo.QueryEvents.querySuccess, function (e, args) {
var hasNoResults = args.results.totalCount === 0;
var isCategoryTabSelected = args.query.tab !== "default";
if (hasNoResults && isCategoryTabSelected) {
var mainSearchInterfaceLayout = getSearchInterfaceLayout(mainSearchInterfaceElement);
setSearchInterfaceLayout(noResultsPopularSearchElement, mainSearchInterfaceLayout);
Coveo.executeQuery(noResultsPopularSearchElement);
showElement(noResultsPopularSection);
} else {
hideElement(noResultsPopularSection);
}
});
Coveo.SearchEndpoint.configureCloudV2Endpoint('default', 'YOUR_API_KEY');
Coveo.init(mainSearchInterfaceElement);
Popular Results Code
On this side, the query to execute must be defined. A buildingQuery event handler is extracting the query expression of the selected main search interface tab and using it to display products from the selected category only.
Coveo.$$(noResultsPopularSearchElement).on(Coveo.QueryEvents.buildingQuery, function (e, args) {
var currentTab = getCurrentTab(mainSearchInterfaceElement);
var tabExpression = currentTab.options.expression;
if (tabExpression) {
var isTabExpressionConstant = !!currentTab.options.constant;
var expressionToAlter = isTabExpressionConstant ? args.queryBuilder.constantExpression : args.queryBuilder.advancedExpression;
expressionToAlter.add(tabExpression);
}
});
Coveo.init(noResultsPopularSearchElement);
Conclusion
It is very easy to act when there are no results thanks to the flexibility of the Coveo JavaScript Search Framework and its event model. The key is the querySuccess event where the number of returned results can be evaluated.
